
The reflecting telescope which uses an arrangement of mirrors to form an image.ģ. The refracting telescope which uses lenses to form an image.Ģ. Optical telescopes are used for astronomy and in many non-astronomical instruments, including: theodolites (including transits), spotting scopes, monoculars, binoculars, camera lenses, and spyglasses. In order for the image to be observed, photographed, studied, and sent to a computer, telescopes work by employing one or more curved optical elements, usually made from glass lenses and/or mirrors, to gather light and other electromagnetic radiation to bring that light or radiation to a focal point. Optical telescopes increase the apparent angular size of distant objects as well as their apparent brightness. Telescopes may be classified by the wavelengths of light they detect:Īn optical telescope gathers and focuses light mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum (although some work in the infrared and ultraviolet). Most detect electromagnetic radiation, but there are major differences in how astronomers must go about collecting light (electromagnetic radiation) in different frequency bands. The name “telescope” covers a wide range of instruments. Credit: Meade The Hubble Space Telescope as seen from the departing Space Shuttle Atlantis, flying Servicing Mission 4 (STS-125), the fifth and latest human spaceflight to it. Meade 114EQ-AR Equatorial Reflector Telescope. Reflecting telescopes range is size – from a backyard telescope to the Hubble telescope in earth orbit. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a “catoptric” telescope.

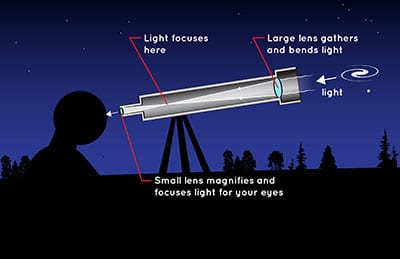
Reflecting telescopes come in many design variations and may employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Credit: WikipediaĪ reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is an optical telescope which uses a single or combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. 8-inch (20 cm) refractor at the Observatories at Chabot Space & Science Center in Oakland, California. Although large refracting telescopes were very popular in the second half of the 19th century, for most research purposes the refracting telescope has been superseded by the reflecting telescope. The refracting telescope design was originally used in spy glasses and astronomical telescopes but is also used for long focus camera lenses. The word telescope now refers to a wide range of instruments detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors.Ī refracting or refractor telescope is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens as its objective to form an image (also referred to a dioptric telescope). In the 20th century many new types of telescopes were invented, including radio telescopes in the 1930s and infrared telescopes in the 1960s. Within a few decades, the reflecting telescope was invented, which used mirrors. They found use in terrestrial applications and astronomy.

The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 17th century, using glass lenses. Image courtesy of Wikipedia.Ī telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation (such as visible light). The height of the observatory above the Atlantic Ocean ensures that it is almost always above the clouds. The Nordic Optical Telescope (NOT) telescope at Roque de los Muchachos Observatory in June 2001.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
